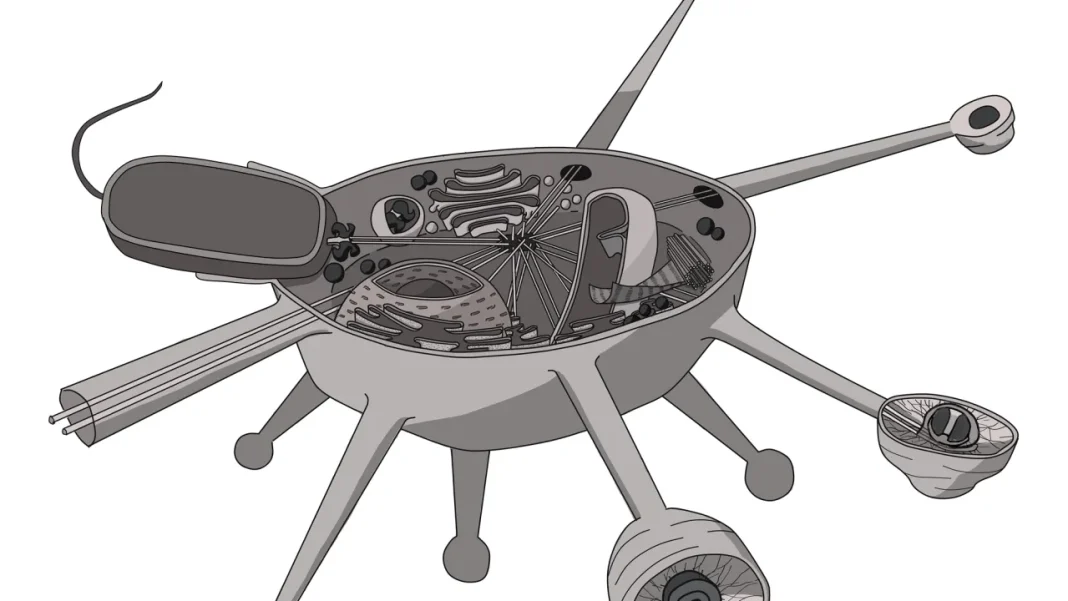
Czech scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery by identifying a protozoan with unique traits. This finding could have significant implications for biological research and understanding these microorganisms.
Discovery and Significance

The recent discovery by a team of Czech scientists revolves around a newly identified protozoan that exhibits characteristics previously unseen in similar organisms. Protozoa, single-celled eukaryotes, are crucial to many ecosystems and have a substantial impact on environmental balances. This particular finding opens avenues for deeper scientific inquiries into how such microorganisms could influence their habitats and interact with other life forms.
The unique traits of this protozoan may lead to a better understanding of complex biological processes. By analyzing its genetic makeup, researchers hope to unveil mechanisms that could shed light on evolution and adaptation. The implications extend beyond pure science and touch on practical applications in medicine and environmental management.
Research Methodology

Conducted at a leading Czech research institute, the study employed advanced microscopy and genetic sequencing techniques. The combination of these methods allowed scientists to observe the protozoan’s behaviors and structures in greater detail than ever before. By isolating the organism in various environments, the team was able to identify its distinct adaptive traits.
The research methodology underscores the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration. Biologists, geneticists, and ecologists worked together to map the protozoan’s unique features, applying both traditional observational tactics and cutting-edge technology to ensure comprehensive results.
Potential Applications
Understanding the unique traits of this protozoan could have far-reaching applications in several fields. In medicine, for instance, insights into protozoan behavior might lead to new treatments for diseases caused by similar organisms. This could revolutionize how we approach certain infections that are resistant to current therapies.
Moreover, the ecological implications are equally promising. By understanding how these protozoans interact within ecosystems, scientists can develop better conservation strategies. This might help in restoring ecological balance in areas disrupted by human activity or climate change.
International Collaboration and Future Research

The discovery has garnered attention from the international scientific community, sparking collaborations between Czech researchers and their global counterparts. This cooperative effort is essential to expand the scope of the study and verify findings across different environments and conditions.
Future research will likely focus on further exploring the protozoan’s genetic material to map out evolutionary pathways and potential applications. Continued international cooperation could accelerate breakthroughs, leading to practical solutions for environmental and health challenges worldwide.
The discovery of this protozoan with unique traits marks an exciting chapter in biological research. As studies progress, the potential for significant benefits in medicine and ecology becomes increasingly evident.
Source: Official [entity name] website.